mixed-reality
Perception simulation
Do you want to build an automated test for your app? Do you want your tests to go beyond component-level unit testing and really exercise your app end-to-end? Perception Simulation is what you’re looking for. The Perception Simulation library sends human and world input data to your app so you can automate your tests. For example, you can simulate the input of a human looking to a specific, repeatable position and then use a gesture or motion controller.
Perception Simulation can send simulated input like this to a physical HoloLens, the HoloLens emulator (first gen), the HoloLens 2 Emulator, or a PC with Mixed Reality Portal installed. Perception Simulation bypasses the live sensors on a Mixed Reality device and sends simulated input to applications running on the device. Applications receive these input events through the same APIs they always use and can’t tell the difference between running with real sensors versus Perception Simulation. Perception Simulation is the same technology used by the HoloLens emulators to send simulated input to the HoloLens Virtual Machine.
To begin using simulation in your code, start by creating an IPerceptionSimulationManager object. From that object, you can issue commands to control properties of a simulated “human”, including head position, hand position, and gestures. You can also enable and manipulate motion controllers.
Setting Up a Visual Studio Project for Perception Simulation
- Install the HoloLens emulator on your development PC. The emulator includes the libraries you’ use for Perception Simulation.
- Create a new Visual Studio C# desktop project (a Console Project works great to get started).
-
Add the following binaries to your project as references (Project->Add->Reference…). You can find them in %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft XDE\(version), such as %ProgramFiles(x86)%\Microsoft XDE\10.0.18362.0 for the HoloLens 2 Emulator.
[!Note] Although the binaries are part of the HoloLens 2 Emulator, they also work for Windows Mixed Reality on the desktop.)
a. PerceptionSimulationManager.Interop.dll - Managed C# wrapper for Perception Simulation.
b. PerceptionSimulationRest.dll - Library for setting up a web-socket communication channel to the HoloLens or emulator.
c. SimulationStream.Interop.dll - Shared types for simulation. -
Add the implementation binary PerceptionSimulationManager.dll to your project
a. First add it as a binary to the project (Project->Add->Existing Item…). Save it as a link so that it doesn’t copy it to your project source folder.
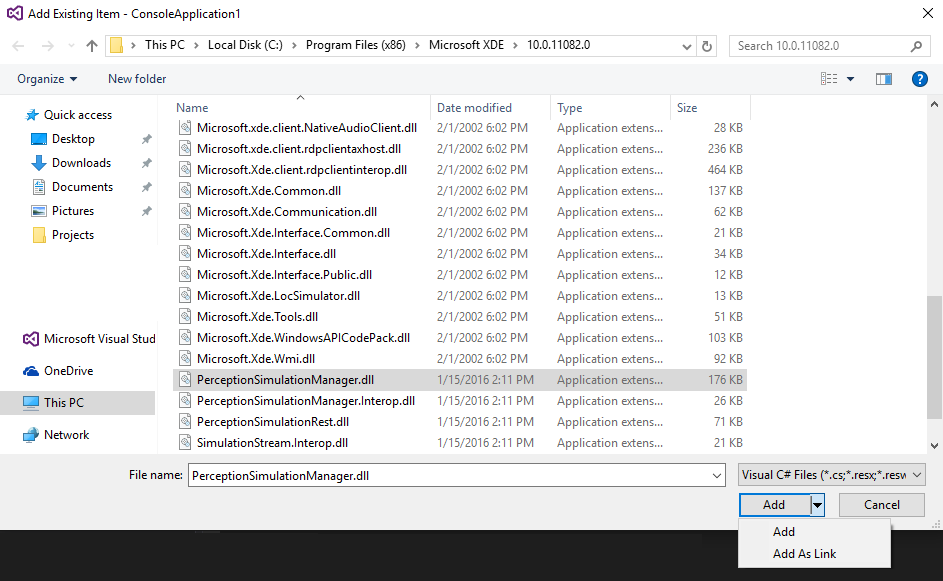
b. Then make sure that it gets copied to your output folder on build. This is in the property sheet for the binary.
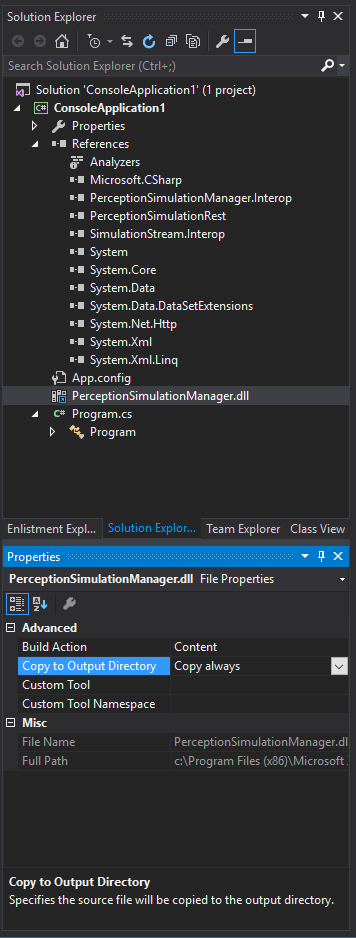
- Set your active solution platform to x64. (Use the Configuration Manager to create a Platform entry for x64 if one doesn’t already exist.)
Creating an IPerceptionSimulation Manager Object
To control simulation, you’ll issue updates to objects retrieved from an IPerceptionSimulationManager object. The first step is to get that object and connect it to your target device or emulator. You can get the IP address of your emulator by clicking on the Device Portal button in the toolbar
 Open Device Portal: Open the Windows Device Portal for the HoloLens OS in the emulator. For Windows Mixed Reality, this can be retrieved in the Settings app under “Update & Security”, then “For developers” in the “Connect using:” section under “Enable Device Portal.” Be sure to note both the IP address and port.
Open Device Portal: Open the Windows Device Portal for the HoloLens OS in the emulator. For Windows Mixed Reality, this can be retrieved in the Settings app under “Update & Security”, then “For developers” in the “Connect using:” section under “Enable Device Portal.” Be sure to note both the IP address and port.
First, you’ll call RestSimulationStreamSink.Create to get a RestSimulationStreamSink object. This is the target device or emulator that you’ll control over an http connection. Your commands will be passed to and handled by the Windows Device Portal running on the device or emulator. The four parameters you’ll need to create an object are:
- Uri uri - IP address of the target device (e.g., “https://123.123.123.123” or “https://123.123.123.123:50080”)
- System.Net.NetworkCredential credentials - Username/password for connecting to the Windows Device Portal on the target device or emulator. If you’re connecting to the emulator via its local address (e.g., 168...*) on the same PC, any credentials will be accepted.
- bool normal - True for normal priority, false for low priority. You generally want to set this to true for test scenarios, which allows your test to take control. The emulator and Windows Mixed Reality simulation use low-priority connections. If your test also uses a low-priority connection, the most recently established connection will be in control.
- System.Threading.CancellationToken token - Token to cancel the async operation.
Second, you’ll create the IPerceptionSimulationManager. This is the object you use to control simulation. This must also be done in an async method.
Control the simulated Human
An IPerceptionSimulationManager has a Human property that returns an ISimulatedHuman object. To control the simulated human, perform operations on this object. For example:
manager.Human.Move(new Vector3(0.1f, 0.0f, 0.0f))
Basic Sample C# console application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Task.Run(async () =>
{
RestSimulationStreamSink sink = null;
CancellationToken token = new System.Threading.CancellationToken();
try
{
sink = await RestSimulationStreamSink.Create(
// use the IP address for your device/emulator
new Uri("https://169.254.227.115"),
// no credentials are needed for the emulator
new System.Net.NetworkCredential("", ""),
// normal priorty
true,
// cancel token
token);
IPerceptionSimulationManager manager = PerceptionSimulationManager.CreatePerceptionSimulationManager(sink);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
// Always close the sink to return control to the previous application.
if (sink != null)
{
await sink.Close(token);
}
});
// If main exits, the process exits.
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Extended Sample C# console application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
RestSimulationStreamSink sink = null;
CancellationToken token = new System.Threading.CancellationToken();
Task.Run(async () =>
{
try
{
sink = await RestSimulationStreamSink.Create(
// use the IP address for your device/emulator
new Uri("https://169.254.227.115"),
// no credentials are needed for the emulator
new System.Net.NetworkCredential("", ""),
// normal priorty
true,
// cancel token
token);
IPerceptionSimulationManager manager = PerceptionSimulationManager.CreatePerceptionSimulationManager(sink);
// Now, we'll simulate a sequence of actions.
// Sleeps in-between each action give time to the system
// to be able to properly react.
// This is just an example. A proper automated test should verify
// that the app has behaved correctly
// before proceeding to the next step, instead of using Sleeps.
// Activate the right hand
manager.Human.RightHand.Activated = true;
// Simulate Bloom gesture, which should cause Shell to disappear
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.Home);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Simulate Bloom gesture again... this time, Shell should reappear
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.Home);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Simulate a Head rotation down around the X axis
// This should cause gaze to aim about the center of the screen
manager.Human.Head.Rotate(new Rotation3(0.04f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
Thread.Sleep(300);
// Simulate a finger press & release
// Should cause a tap on the center tile, thus launching it
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.FingerPressed);
Thread.Sleep(300);
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.FingerReleased);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Simulate a second finger press & release
// Should activate the app that was launched when the center tile was clicked
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.FingerPressed);
Thread.Sleep(300);
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.FingerReleased);
Thread.Sleep(5000);
// Simulate a Head rotation towards the upper right corner
manager.Human.Head.Rotate(new Rotation3(-0.14f, 0.17f, 0.0f));
Thread.Sleep(300);
// Simulate a third finger press & release
// Should press the Remove button on the app
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.FingerPressed);
Thread.Sleep(300);
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.FingerReleased);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Simulate Bloom gesture again... bringing the Shell back once more
manager.Human.RightHand.PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture.Home);
Thread.Sleep(2000);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
});
// If main exits, the process exits.
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadLine();
// Always close the sink to return control to the previous application.
if (sink != null)
{
sink.Close(token);
}
}
}
}
Note on 6-DOF controllers
Before calling any properties on methods on a simulated 6-DOF controller, you must activate the controller. Not doing so will result in an exception. Starting with the Windows 10 May 2019 Update, simulated 6-DOF controllers can be installed and activated by setting the Status property on the ISimulatedSixDofController object to SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus.Active. In the Windows 10 October 2018 Update and earlier, you must separately install a simulated 6-DOF controller first by calling the PerceptionSimulationDevice tool located in the \Windows\System32 folder. The usage of this tool is as follows:
PerceptionSimulationDevice.exe <action> 6dof <instance>
For example
PerceptionSimulationDevice.exe i 6dof 1
Supported actions are:
- i = install
- q = query
- r = remove
Supported instances are:
- 1 = the left 6-DOF controller
- 2 = the right 6-DOF controller
The exit code of the process will indicate success (a zero return value) or failure (a non-zero return value). When using the ‘q’ action to query whether a controller is installed, the return value will be zero (0) if the controller isn’t already installed or one (1) if the controller is installed.
When removing a controller on the Windows 10 October 2018 Update or earlier, set its status to Off via the API first, then call the PerceptionSimulationDevice tool.
This tool must be run as Administrator.
API Reference
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDeviceType
Describes a simulated device type
public enum SimulatedDeviceType
{
Reference = 0
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDeviceType.Reference
A fictitious reference device, the default for PerceptionSimulationManager
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.HeadTrackerMode
Describes a head tracker mode
public enum HeadTrackerMode
{
Default = 0,
Orientation = 1,
Position = 2
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.HeadTrackerMode.Default
Default Head Tracking. This means the system may select the best head tracking mode based upon runtime conditions.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.HeadTrackerMode.Orientation
Orientation Only Head Tracking. This means that the tracked position may not be reliable, and some functionality dependent on head position may not be available.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.HeadTrackerMode.Position
Positional Head Tracking. This means that the tracked head position and orientation are both reliable
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture
Describes a simulated gesture
public enum SimulatedGesture
{
None = 0,
FingerPressed = 1,
FingerReleased = 2,
Home = 4,
Max = Home
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture.None
A sentinel value used to indicate no gestures.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture.FingerPressed
A finger pressed gesture.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture.FingerReleased
A finger released gesture.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture.Home
The home/system gesture.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture.Max
The maximum valid gesture.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus
The possible states of a simulated 6-DOF controller.
public enum SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus
{
Off = 0,
Active = 1,
TrackingLost = 2,
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus.Off
The 6-DOF controller is turned off.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus.Active
The 6-DOF controller is turned on and tracked.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus.TrackingLost
The 6-DOF controller is turned on but cannot be tracked.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton
The supported buttons on a simulated 6-DOF controller.
public enum SimulatedSixDofControllerButton
{
None = 0,
Home = 1,
Menu = 2,
Grip = 4,
TouchpadPress = 8,
Select = 16,
TouchpadTouch = 32,
Thumbstick = 64,
Max = Thumbstick
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.None
A sentinel value used to indicate no buttons.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.Home
The Home button is pressed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.Menu
The Menu button is pressed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.Grip
The Grip button is pressed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.TouchpadPress
The TouchPad is pressed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.Select
The Select button is pressed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.TouchpadTouch
The TouchPad is touched.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.Thumbstick
The Thumbstick is pressed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedSixDofControllerButton.Max
The maximum valid button.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedEyesCalibrationState
The calibration state of the simulated eyes
public enum SimulatedGesture
{
Unavailable = 0,
Ready = 1,
Configuring = 2,
UserCalibrationNeeded = 3
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedEyesCalibrationState.Unavailable
The eyes calibration is unavailable.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedEyesCalibrationState.Ready
The eyes have been calibrated. This is the default value.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedEyesCalibrationState.Configuring
The eyes are being calibrated.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedEyesCalibrationState.UserCalibrationNeeded
The eyes need to be calibrated.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointTrackingAccuracy
The tracking accuracy of a joint of the hand.
public enum SimulatedHandJointTrackingAccuracy
{
Unavailable = 0,
Approximate = 1,
Visible = 2
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointTrackingAccuracy.Unavailable
The joint isn’t tracked.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointTrackingAccuracy.Approximate
The joint position is inferred.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointTrackingAccuracy.Visible
The joint is fully tracked.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandPose
The tracking accuracy of a joint of the hand.
public enum SimulatedHandPose
{
Closed = 0,
Open = 1,
Point = 2,
Pinch = 3,
Max = Pinch
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandPose.Closed
The hand’s finger joints are configured to reflect a closed pose.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandPose.Open
The hand’s finger joints are configured to reflect an open pose.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandPose.Point
The hand’s finger joints are configured to reflect a pointing pose.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandPose.Pinch
The hand’s finger joints are configured to reflect a pinching pose.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandPose.Max
The maximum valid value for SimulatedHandPose.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PlaybackState
Describes the state of a playback.
public enum PlaybackState
{
Stopped = 0,
Playing = 1,
Paused = 2,
End = 3,
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PlaybackState.Stopped
The recording is currently stopped and ready for playback.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PlaybackState.Playing
The recording is currently playing.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PlaybackState.Paused
The recording is currently paused.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PlaybackState.End
The recording has reached the end.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3
Describes a three components vector, which might describe a point or a vector in 3D space.
public struct Vector3
{
public float X;
public float Y;
public float Z;
public Vector3(float x, float y, float z);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3.X
The X component of the vector.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3.Y
The Y component of the vector.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3.Z
The Z component of the vector.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3.#ctor(System.Single,System.Single,System.Single)
Construct a new Vector3.
Parameters
- x - The x component of the vector.
- y - The y component of the vector.
- z - The z component of the vector.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3
Describes a three components rotation.
public struct Rotation3
{
public float Pitch;
public float Yaw;
public float Roll;
public Rotation3(float pitch, float yaw, float roll);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3.Pitch
The Pitch component of the Rotation, down around the X axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3.Yaw
The Yaw component of the Rotation, right around the Y axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3.Roll
The Roll component of the Rotation, right around the Z axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3.#ctor(System.Single,System.Single,System.Single)
Construct a new Rotation3.
Parameters
- pitch - The pitch component of the Rotation.
- yaw - The yaw component of the Rotation.
- roll - The roll component of the Rotation.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointConfiguration
Describes the configuration of a joint on a simulated hand.
public struct SimulatedHandJointConfiguration
{
public Vector3 Position;
public Rotation3 Rotation;
public SimulatedHandJointTrackingAccuracy TrackingAccuracy;
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointConfiguration.Position
The position of the joint.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointConfiguration.Rotation
The rotation of the joint.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedHandJointConfiguration.TrackingAccuracy
The tracking accuracy of the joint.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Frustum
Describes a view frustum, as typically used by a camera.
public struct Frustum
{
float Near;
float Far;
float FieldOfView;
float AspectRatio;
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Frustum.Near
The minimum distance that is contained in the frustum.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Frustum.Far
The maximum distance that is contained in the frustum.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Frustum.FieldOfView
The horizontal field of view of the frustum, in radians (less than PI).
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Frustum.AspectRatio
The ratio of horizontal field of view to vertical field of view.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration
Describes the configuration of the simulated headset’s display.
public struct SimulatedDisplayConfiguration
{
public Vector3 LeftEyePosition;
public Rotation3 LeftEyeRotation;
public Vector3 RightEyePosition;
public Rotation3 RightEyeRotation;
public float Ipd;
public bool ApplyEyeTransforms;
public bool ApplyIpd;
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.LeftEyePosition
The transform from the center of the head to the left eye for purposes of stereo rendering.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.LeftEyeRotation
The rotation of the left eye for purposes of stereo rendering.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.RightEyePosition
The transform from the center of the head to the right eye for purposes of stereo rendering.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.RightEyeRotation
The rotation of the right eye for purposes of stereo rendering.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.Ipd
The Ipd value reported by the system for purposes of stereo rendering.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.ApplyEyeTransforms
Whether the values provided for left and right eye transforms should be considered valid and applied to the running system.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDisplayConfiguration.ApplyIpd
Whether the value provided for Ipd should be considered valid and applied to the running system.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.IPerceptionSimulationManager
Root for generating the packets used to control a device.
public interface IPerceptionSimulationManager
{
ISimulatedDevice Device { get; }
ISimulatedHuman Human { get; }
void Reset();
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.IPerceptionSimulationManager.Device
Retrieve the simulated device object that interprets the simulated human and the simulated world.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.IPerceptionSimulationManager.Human
Retrieve the object that controls the simulated human.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.IPerceptionSimulationManager.Reset
Resets the simulation to its default state.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice
Interface describing the device, which interprets the simulated world and the simulated human
public interface ISimulatedDevice
{
ISimulatedHeadTracker HeadTracker { get; }
ISimulatedHandTracker HandTracker { get; }
void SetSimulatedDeviceType(SimulatedDeviceType type);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice.HeadTracker
Retrieve the Head Tracker from the Simulated Device.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice.HandTracker
Retrieve the Hand Tracker from the Simulated Device.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice.SetSimulatedDeviceType(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedDeviceType)
Set the properties of the simulated device to match the provided device type.
Parameters
- type - The new type of Simulated Device
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice2
Additional properties are available by casting the ISimulatedDevice to ISimulatedDevice2
public interface ISimulatedDevice2
{
bool IsUserPresent { [return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] get; [param: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] set; }
SimulatedDisplayConfiguration DisplayConfiguration { get; set; }
};
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice2.IsUserPresent
Retrieve or set whether or not the simulated human is actively wearing the headset.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedDevice2.DisplayConfiguration
Retrieve or set the properties of the simulated display.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHeadTracker
Interface describing the portion of the simulated device that tracks the head of the simulated human.
public interface ISimulatedHeadTracker
{
HeadTrackerMode HeadTrackerMode { get; set; }
};
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHeadTracker.HeadTrackerMode
Retrieves and sets the current head tracker mode.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHandTracker
Interface describing the portion of the simulated device that tracks the hands of the simulated human
public interface ISimulatedHandTracker
{
Vector3 WorldPosition { get; }
Vector3 Position { get; set; }
float Pitch { get; set; }
bool FrustumIgnored { [return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] get; [param: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] set; }
Frustum Frustum { get; set; }
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHandTracker.WorldPosition
Retrieve the position of the node with relation to the world, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHandTracker.Position
Retrieve and set the position of the simulated hand tracker, relative to the center of the head.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHandTracker.Pitch
Retrieve and set the downward pitch of the simulated hand tracker.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHandTracker.FrustumIgnored
Retrieve and set whether the frustum of the simulated hand tracker is ignored. When ignored, both hands are always visible. When not ignored (the default) hands are only visible when they are within the frustum of the hand tracker.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHandTracker.Frustum
Retrieve and set the frustum properties used to determine if hands are visible to the simulated hand tracker.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman
Top-level interface for controlling the simulated human.
public interface ISimulatedHuman
{
Vector3 WorldPosition { get; set; }
float Direction { get; set; }
float Height { get; set; }
ISimulatedHand LeftHand { get; }
ISimulatedHand RightHand { get; }
ISimulatedHead Head { get; }s
void Move(Vector3 translation);
void Rotate(float radians);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.WorldPosition
Retrieve and set the position of the node with relation to the world, in meters. The position corresponds to a point at the center of the human’s feet.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.Direction
Retrieve and set the direction the simulated human faces in the world. 0 radians faces down the negative Z axis. Positive radians rotate clockwise about the Y axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.Height
Retrieve and set the height of the simulated human, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.LeftHand
Retrieve the left hand of the simulated human.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.RightHand
Retrieve the right hand of the simulated human.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.Head
Retrieve the head of the simulated human.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.Move(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3)
Move the simulated human relative to its current position, in meters.
Parameters
- translation - The translation to move, relative to current position.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman.Rotate(System.Single)
Rotate the simulated human relative to its current direction, clockwise about the Y axis
Parameters
- radians - The amount to rotate around the Y axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman2
Additional properties are available by casting the ISimulatedHuman to ISimulatedHuman2
public interface ISimulatedHuman2
{
/* New members in addition to those available on ISimulatedHuman */
ISimulatedSixDofController LeftController { get; }
ISimulatedSixDofController RightController { get; }
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman2.LeftController
Retrieve the left 6-DOF controller.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHuman2.RightController
Retrieve the right 6-DOF controller.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand
Interface describing a hand of the simulated human
public interface ISimulatedHand
{
Vector3 WorldPosition { get; }
Vector3 Position { get; set; }
bool Activated { [return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] get; [param: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] set; }
bool Visible { [return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] get; }
void EnsureVisible();
void Move(Vector3 translation);
void PerformGesture(SimulatedGesture gesture);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.WorldPosition
Retrieve the position of the node with relation to the world, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.Position
Retrieve and set the position of the simulated hand relative to the human, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.Activated
Retrieve and set whether the hand is currently activated.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.Visible
Retrieve whether the hand is currently visible to the SimulatedDevice (that is, whether it’s in a position to be detected by the HandTracker).
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.EnsureVisible
Move the hand such that it is visible to the SimulatedDevice.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.Move(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3)
Move the position of the simulated hand relative to its current position, in meters.
Parameters
- translation - The amount to translate the simulated hand.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand.PerformGesture(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.SimulatedGesture)
Perform a gesture using the simulated hand. It will only be detected by the system if the hand is enabled.
Parameters
- gesture - The gesture to perform.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand2
Additional properties are available by casting an ISimulatedHand to ISimulatedHand2.
public interface ISimulatedHand2
{
/* New members in addition to those available on ISimulatedHand */
Rotation3 Orientation { get; set; }
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand2.Orientation
Retrieve or set the rotation of the simulated hand. Positive radians rotate clockwise when looking along the axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand3
Additional properties are available by casting an ISimulatedHand to ISimulatedHand3
public interface ISimulatedHand3
{
/* New members in addition to those available on ISimulatedHand and ISimulatedHand2 */
GetJointConfiguration(SimulatedHandJoint joint, out SimulatedHandJointConfiguration jointConfiguration);
SetJointConfiguration(SimulatedHandJoint joint, SimulatedHandJointConfiguration jointConfiguration);
SetHandPose(SimulatedHandPose pose, bool animate);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand3.GetJointConfiguration
Get the joint configuration for the specified joint.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand3.SetJointConfiguration
Set the joint configuration for the specified joint.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHand3.SetHandPose
Set the hand to a known pose with an optional flag to animate. Note: animating won’t result in joints immediately reflecting their final joint configurations.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead
Interface describing the head of the simulated human.
public interface ISimulatedHead
{
Vector3 WorldPosition { get; }
Rotation3 Rotation { get; set; }
float Diameter { get; set; }
void Rotate(Rotation3 rotation);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead.WorldPosition
Retrieve the position of the node with relation to the world, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead.Rotation
Retrieve the rotation of the simulated head. Positive radians rotate clockwise when looking along the axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead.Diameter
Retrieve the simulated head’s diameter. This value is used to determine the head’s center (point of rotation).
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead.Rotate(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3)
Rotate the simulated head relative to its current rotation. Positive radians rotate clockwise when looking along the axis.
Parameters
- rotation - The amount to rotate.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead2
Additional properties are available by casting an ISimulatedHead to ISimulatedHead2
public interface ISimulatedHead2
{
/* New members in addition to those available on ISimulatedHead */
ISimulatedEyes Eyes { get; }
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedHead2.Eyes
Retrieve the eyes of the simulated human.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController
Interface describing a 6-DOF controller associated with the simulated human.
public interface ISimulatedSixDofController
{
Vector3 WorldPosition { get; }
SimulatedSixDofControllerStatus Status { get; set; }
Vector3 Position { get; }
Rotation3 Orientation { get; set; }
void Move(Vector3 translation);
void PressButton(SimulatedSixDofControllerButton button);
void ReleaseButton(SimulatedSixDofControllerButton button);
void GetTouchpadPosition(out float x, out float y);
void SetTouchpadPosition(float x, float y);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.WorldPosition
Retrieve the position of the node with relation to the world, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.Status
Retrieve or set the current state of the controller. The controller status must be set to a value other than Off before any calls to move, rotate, or press buttons will succeed.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.Position
Retrieve or set the position of the simulated controller relative to the human, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.Orientation
Retrieve or set the orientation of the simulated controller.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.Move(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Vector3)
Move the position of the simulated controller relative to its current position, in meters.
Parameters
- translation - The amount to translate the simulated controller.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.PressButton(SimulatedSixDofControllerButton)
Press a button on the simulated controller. It will only be detected by the system if the controller is enabled.
Parameters
- button - The button to press.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.ReleaseButton(SimulatedSixDofControllerButton)
Release a button on the simulated controller. It will only be detected by the system if the controller is enabled.
Parameters
- button - The button to release.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.GetTouchpadPosition(out float, out float)
Get the position of a simulated finger on the simulated controller’s touchpad.
Parameters
- x - The horizontal position of the finger.
- y - The vertical position of the finger.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController.SetTouchpadPosition(float, float)
Set the position of a simulated finger on the simulated controller’s touchpad.
Parameters
- x - The horizontal position of the finger.
- y - The vertical position of the finger.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController2
Additional properties and methods are available by casting an ISimulatedSixDofController to ISimulatedSixDofController2
public interface ISimulatedSixDofController2
{
/* New members in addition to those available on ISimulatedSixDofController */
void GetThumbstickPosition(out float x, out float y);
void SetThumbstickPosition(float x, float y);
float BatteryLevel { get; set; }
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController2.GetThumbstickPosition(out float, out float)
Get the position of the simulated thumbstick on the simulated controller.
Parameters
- x - The horizontal position of the thumbstick.
- y - The vertical position of the thumbstick.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController2.SetThumbstickPosition(float, float)
Set the position of the simulated thumbstick on the simulated controller.
Parameters
- x - The horizontal position of the thumbstick.
- y - The vertical position of the thumbstick.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedSixDofController2.BatteryLevel
Retrieve or set the battery level of the simulated controller. The value must be greater than 0.0 and less than or equal to 100.0.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedEyes
Interface describing the eyes of the simulated human.
public interface ISimulatedEyes
{
Rotation3 Rotation { get; set; }
void Rotate(Rotation3 rotation);
SimulatedEyesCalibrationState CalibrationState { get; set; }
Vector3 WorldPosition { get; }
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedEyes.Rotation
Retrieve the rotation of the simulated eyes. Positive radians rotate clockwise when looking along the axis.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedEyes.Rotate(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.Rotation3)
Rotate the simulated eyes relative to its current rotation. Positive radians rotate clockwise when looking along the axis.
Parameters
- rotation - The amount to rotate.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedEyes.CalibrationState
Retrieves or sets the calibration state of the simulated eyes.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulatedEyes.WorldPosition
Retrieve the position of the node with relation to the world, in meters.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording
Interface for interacting with a single recording loaded for playback.
public interface ISimulationRecording
{
StreamDataTypes DataTypes { get; }
PlaybackState State { get; }
void Play();
void Pause();
void Seek(UInt64 ticks);
void Stop();
};
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording.DataTypes
Retrieves the list of data types in the recording.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording.State
Retrieves the current state of the recording.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording.Play
Start the playback. If the recording is paused, playback will resume from the paused location; if stopped, playback will start at the beginning. If already playing, this call is ignored.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording.Pause
Pauses the playback at its current location. If the recording is stopped, the call is ignored.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording.Seek(System.UInt64)
Seeks the recording to the specified time (in 100-nanoseconds intervals from the beginning) and pauses at that location. If the time is beyond the end of the recording, it’s paused at the last frame.
Parameters
- ticks - The time to which to seek.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecording.Stop
Stops the playback and resets the position to the beginning.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecordingCallback
Interface for receiving state changes during playback.
public interface ISimulationRecordingCallback
{
void PlaybackStateChanged(PlaybackState newState);
};
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecordingCallback.PlaybackStateChanged(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PlaybackState)
Called when an ISimulationRecording’s playback state has changed.
Parameters
- newState - The new state of the recording.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PerceptionSimulationManager
Root object for creating Perception Simulation objects.
public static class PerceptionSimulationManager
{
public static IPerceptionSimulationManager CreatePerceptionSimulationManager(ISimulationStreamSink sink);
public static ISimulationStreamSink CreatePerceptionSimulationRecording(string path);
public static ISimulationRecording LoadPerceptionSimulationRecording(string path, ISimulationStreamSinkFactory factory);
public static ISimulationRecording LoadPerceptionSimulationRecording(string path, ISimulationStreamSinkFactory factory, ISimulationRecordingCallback callback);
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PerceptionSimulationManager.CreatePerceptionSimulationManager(Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSink)
Create on object for generating simulated packets and delivering them to the provided sink.
Parameters
- sink - The sink that will receive all generated packets.
Return value
The created Manager.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PerceptionSimulationManager.CreatePerceptionSimulationRecording(System.String)
Create a sink, which stores all received packets in a file at the specified path.
Parameters
- path - The path of the file to create.
Return value
The created sink.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PerceptionSimulationManager.LoadPerceptionSimulationRecording(System.String,Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSinkFactory)
Load a recording from the specified file.
Parameters
- path - The path of the file to load.
- factory - A factory used by the recording for creating an ISimulationStreamSink when required.
Return value
The loaded recording.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.PerceptionSimulationManager.LoadPerceptionSimulationRecording(System.String,Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSinkFactory,Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationRecordingCallback)
Load a recording from the specified file.
Parameters
- path - The path of the file to load.
- factory - A factory used by the recording for creating an ISimulationStreamSink when required.
- callback - A callback, which receives updates regrading the recording’s status.
Return value
The loaded recording.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes
Describes the different types of stream data.
public enum StreamDataTypes
{
None = 0x00,
Head = 0x01,
Hands = 0x02,
SpatialMapping = 0x08,
Calibration = 0x10,
Environment = 0x20,
SixDofControllers = 0x40,
Eyes = 0x80,
DisplayConfiguration = 0x100
All = None | Head | Hands | SpatialMapping | Calibration | Environment | SixDofControllers | Eyes | DisplayConfiguration
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.None
A sentinel value used to indicate no stream data types.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.Head
Stream of data for the position and orientation of the head.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.Hands
Stream of data for the position and gestures of hands.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.SpatialMapping
Stream of data for spatial mapping of the environment.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.Calibration
Stream of data for calibration of the device. Calibration packets are only accepted by a system in Remote Mode.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.Environment
Stream of data for the environment of the device.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.SixDofControllers
Stream of data for motion controllers.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.Eyes
Stream of data with the eyes of the simulated human.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.DisplayConfiguration
Stream of data with the display configuration of the device.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.StreamDataTypes.All
A sentinel value used to indicate all recorded data types.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSink
An object that receives data packets from a simulation stream.
public interface ISimulationStreamSink
{
void OnPacketReceived(uint length, byte[] packet);
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSink.OnPacketReceived(uint length, byte[] packet)
Receives a single packet, which is internally typed and versioned.
Parameters
- length - The length of the packet.
- packet - The data of the packet.
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSinkFactory
An object that creates ISimulationStreamSink.
public interface ISimulationStreamSinkFactory
{
ISimulationStreamSink CreateSimulationStreamSink();
}
Microsoft.PerceptionSimulation.ISimulationStreamSinkFactory.CreateSimulationStreamSink()
Creates a single instance of ISimulationStreamSink.
Return value
The created sink.